Stand Restrictions and DMZ Overlays
Overview
Restrictions prevent changes being made to a stand or activity in Spatial ai that would result in a conflict of data. Spatial ai provides three separate means to record or check for restrictions placed on a stand, the first being a manual tabular restriction that can be added via the stand attributes form. The second is a system restriction created upon the completion of certain activities. Finally, the third is from an overlapping of features in the stands layer with features in the DMZ (Delicate Management Zone) layer. This will cover these three methods as well as their impacts on activities.
Need More Help?
For personalized assistance tailored to your specific needs, speak with a knowledgeable customer service representative.
Workflows
Stand Restrictions
Tabular Stand Restrictions
A manual tabular restriction can be added via the stand attribute form by any user with appropriate permissions. This restriction can be edited or removed by the user at any time.
Step 1: From the left-side menu in the Stand Attribute form, select “Restrictions.”
Step 2: Select the green “New” button at the bottom of the Stand Attribute form.
Step 3: Select Restriction Type, Fill in Beginning Date, Exp Date, and comment (required)
Step 4: Optional – check never expires if this is a permanent restriction; or add Enforce months for partial year restrictions.
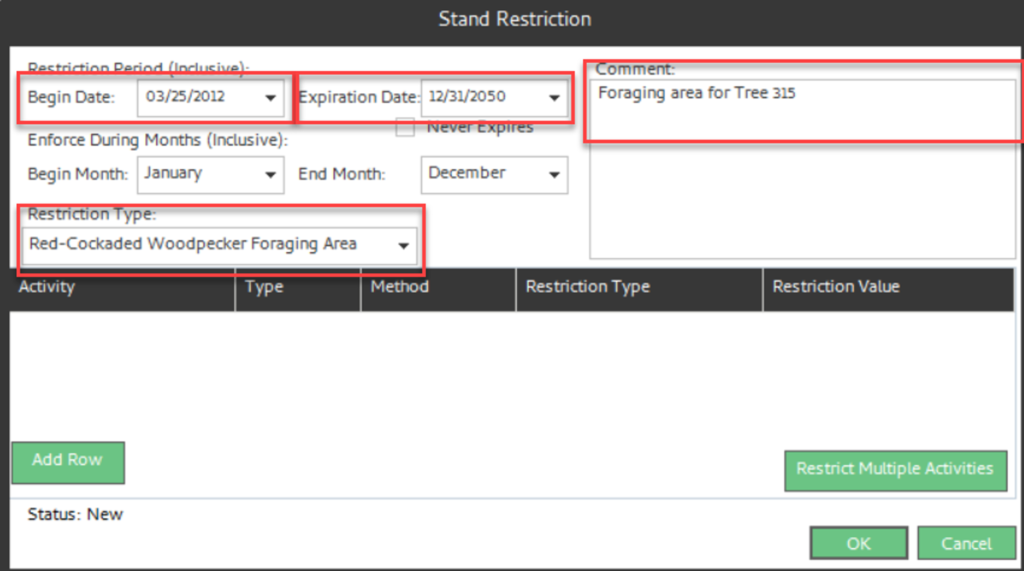
Step 5: Now select activities to restrict, using one of the following methods:
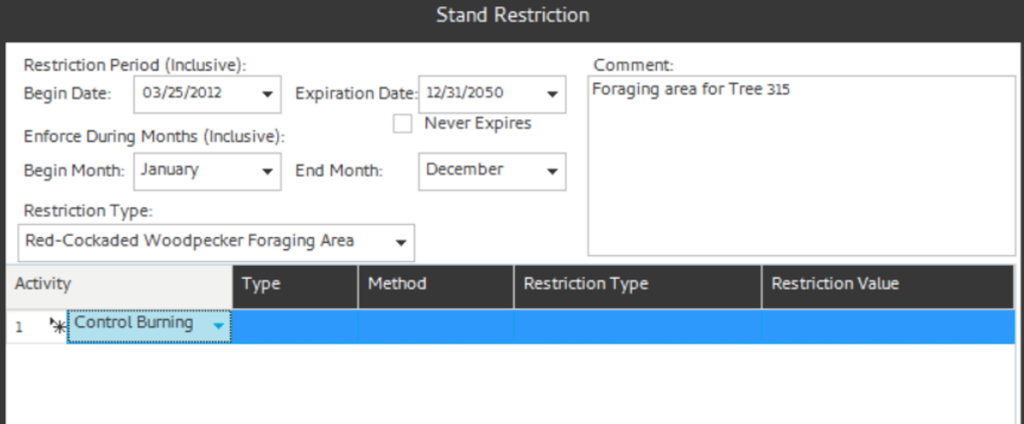
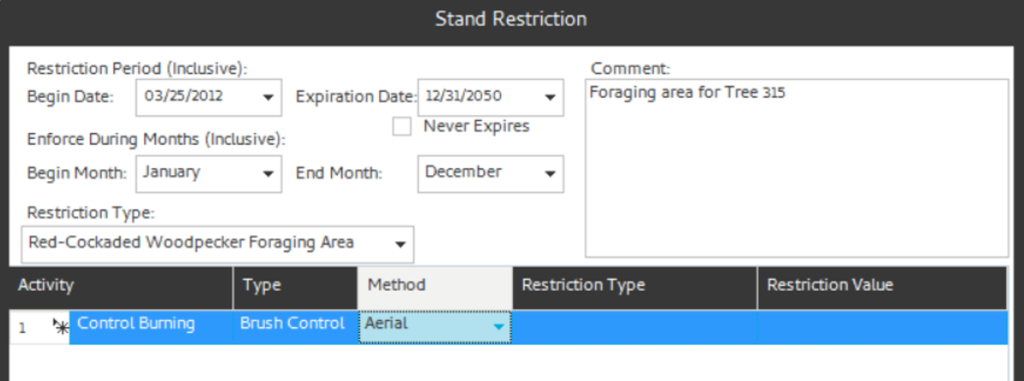
- Method 1: Add a single row at a time by clicking the “Add Row” button in the lower left corner. This adds a single row with drop downs to select an Activity. You can restrict all Activity-Type-Methods by just adding the activity or you can select specific Activity-Type-Methods by adding Type or Type-Method.
- Method 2: Click the “Add Multiple Activities” button on the lower right. This displays a complete list of Activities to select from.
The selected activities are added. The Logging activity requires a restriction type (BA, Percent, Stems) and an associate value.
Step 6: Click “OK” to save your work.
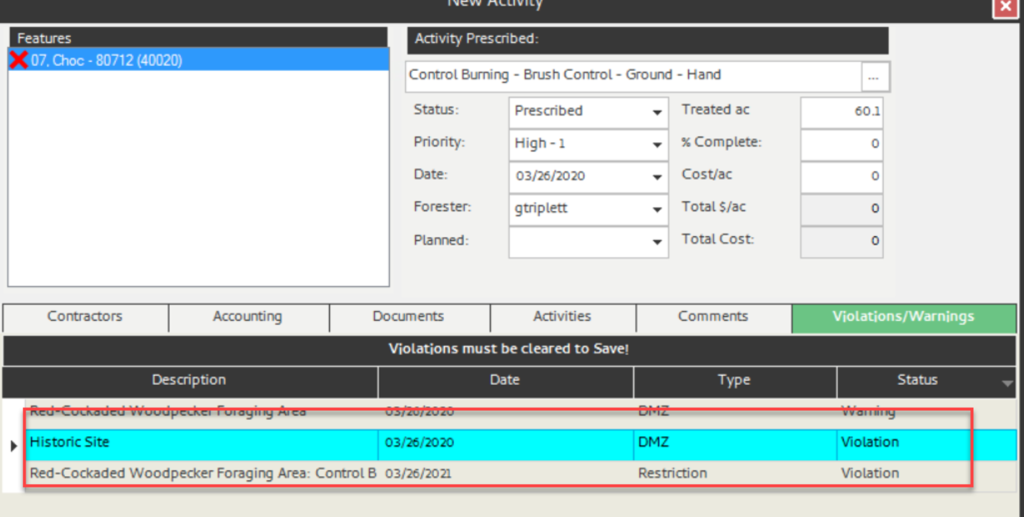
Note: If you run the DMZ report now on the selected stand, you will see the single stand restriction (shown left). Additionally, trying to prescribe Understory Brush Control displays the violation (shown right).
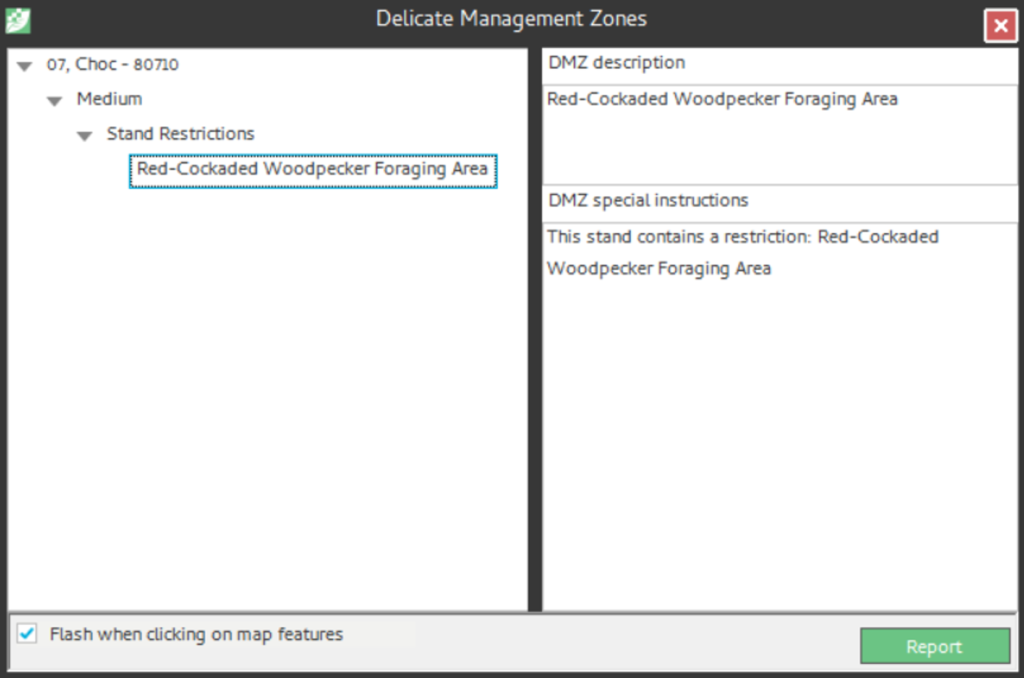
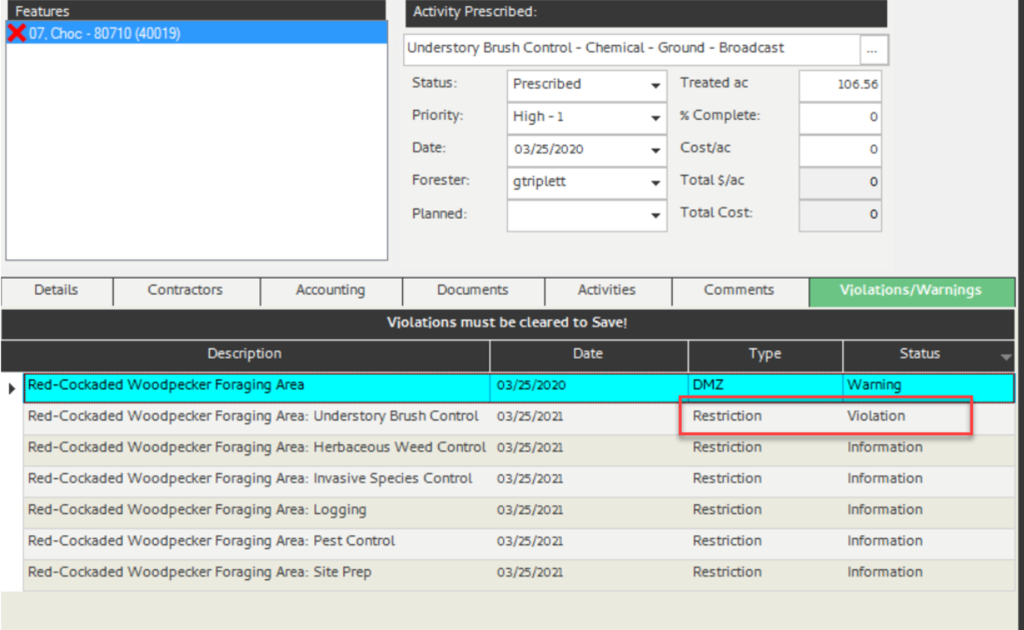
System Generated Restrictions
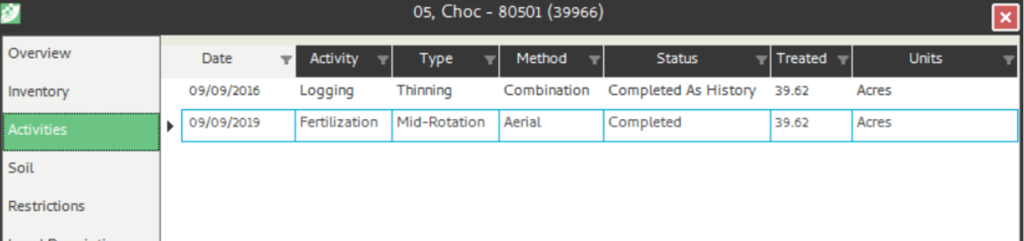
Upon completion of certain silvicultural activities, the system can auto generate restrictions for those stands impacted. An example of this would be a system generated restriction that is created upon the completion of a fertilization. In this example, the system will generate a restriction on control burning and logging for 36 months. System generated restrictions are configurable and these configurations are usually done during initial database population by your setup group or your system administrator. However, system generated restrictions can be updated at any time by your system administrator.
Example) A system generated restriction has been set up for a completed Fertilization activity as defined in the example below.
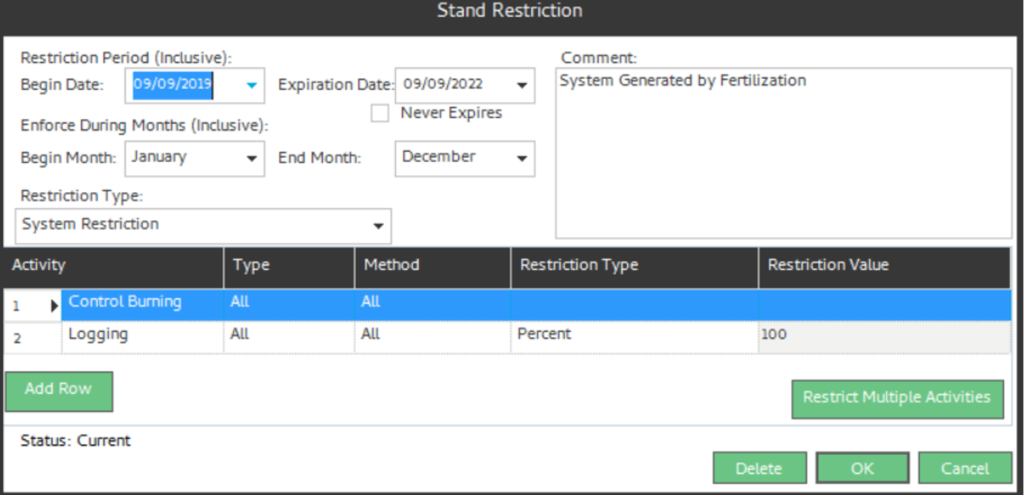
- The system generated restriction will look like the image below on the Stand Restriction form.
DMZ Warning and Restrictions
The stand restrictions described above are purely tabular and must be entered manually. Spatial AI, however, also has the ability to spatially check for warnings and restrictions via spatial overlay against other layers managed within the system. Your organization may have a biologist or environmentalist that maintains layers of species or other environmentally sensitive areas. These special data layers may be periodically updated with new locations and boundaries and your organization may desire to manage, maintain, and visualize this data within the spatial system. Spatial AI can house and maintain these spatial layers and the Spatial AI DMZ functionality can handle these changes and prompt the user with warnings and restrictions messages via spatial overlays.
Setting Up Dynamic Standard Layers (DSLs)
Spatial AI typically deploys with a set of DSLs configured to participate in the DMZ process, but others can be added at the discretion of your organization. The standard DSL layers deployed with Spatial AI include:
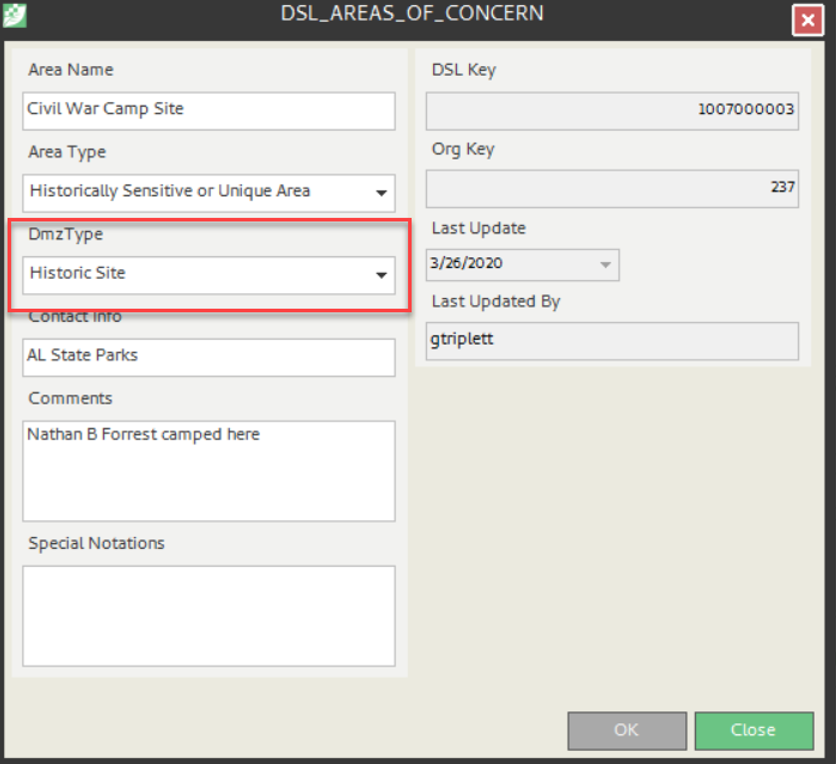
- DSL_Areas_Of_Concern – Polygon – Historical sites, military area, non-specie specific areas
- DSL_Points_of_Concern – Point – Historical sites, military area, non-specie specific points
- DSL_Cemetery – Point – Cemeteries
- DSL_Species_Pts_Of_Concern – Point – Specie specific point location
- DSL_Species_Areas_of_Concern– Polygon – Specie specific area location
- DSL_Reasearch_Area – Polygon – Research areas
On the input form for each of these layers is a dropdown for DMZ Type. Each DMZ Type can be configured by your administrator for both severity and buffer distance. Each Type can also have multiple buffer distances configured.
Running the DMZ Report in Spatial AI
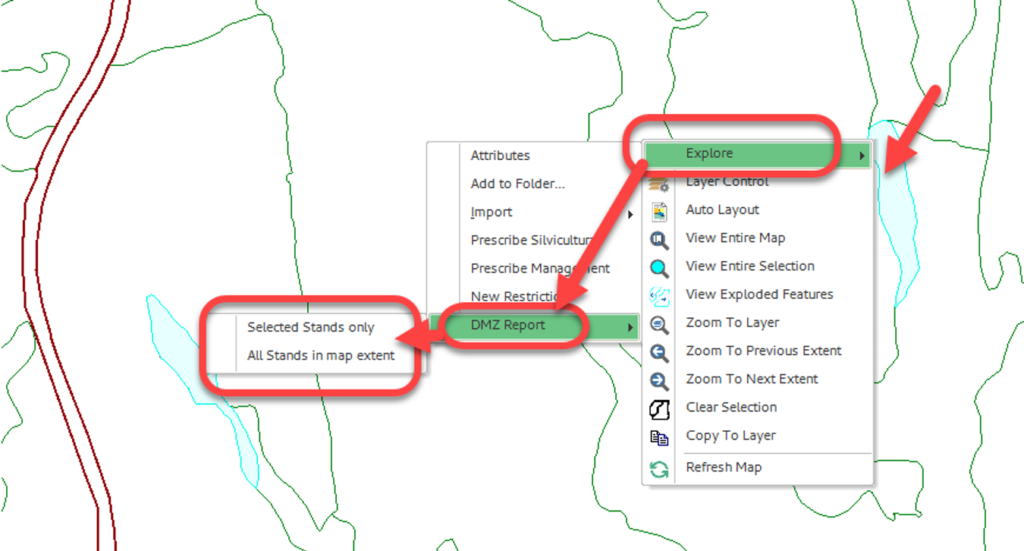
You may run a DMZ report for selected features or for the full map view extent. To run the DMZ report for a selected feature, follow these steps.
To run the DMZ report:
- Select the feature you wish to run the report on in the Map Frame
- Right-click to open the menu
- Select “Explore”
- Select “DMZ Report” from the sub-menu
- Select “Selected Stands Only” if you want to run the report for just the selected features OR select “All Stands in Map Extent” if you want to run the DMZ for all features visible in the Map Frame.
Expected Results:
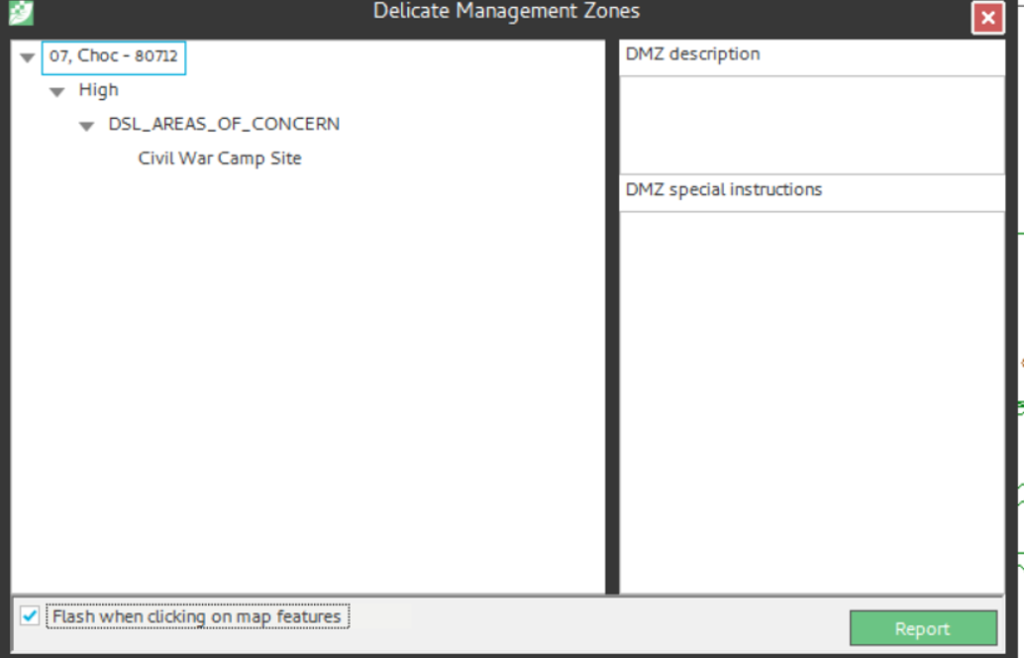
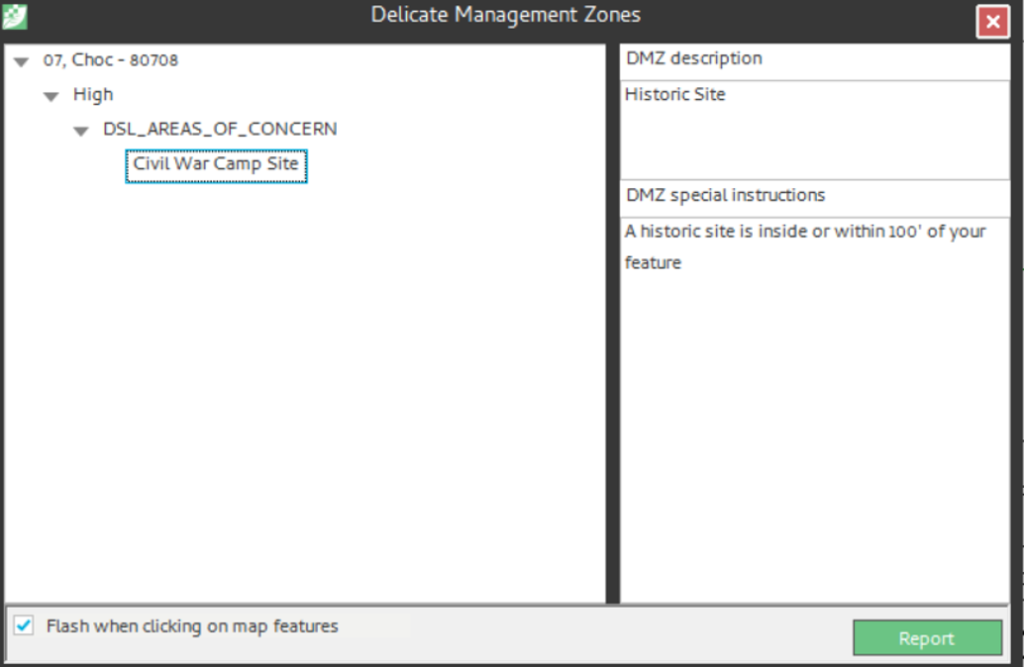
Note: If the stand has a tabular stand restriction, it is returned in the DMZ report as well. The DSL layer does not have to be visible in the Map View or active in the Map TOC, as the DMZ is reporting against the database and not the opened and/or active map layers.
Additionally, when prescribing a silvicultural activity, as above with the tabular stand restrictions, the DMZ runs as well and returns any warnings or violations either spatially or tabularly (shown below).